.png)
Our customer support team is here to answer your questions. Ask us anything!
Chat with us on WhatsApp
Written By: Flipbz.org
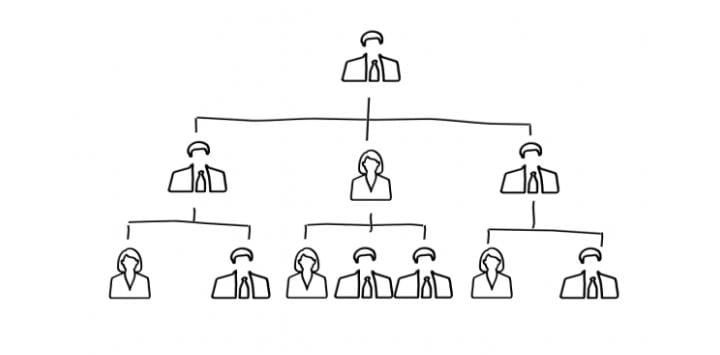
Organizational structure is the system that defines how tasks, responsibilities, and authority are allocated, coordinated, and monitored within an organization. It provides a framework for achieving a company’s goals and outlines how employees work together to accomplish tasks efficiently. An effective organizational structure not only fosters clear communication and accountability but also ensures adaptability in a dynamic business environment. This article will explore the key components, types, benefits, and challenges of organizational structures.
An organizational structure typically involves the following components:
1. Hierarchy of Authority: This defines who reports to whom and ensures that decision-making processes are clear. It creates levels of management and establishes chains of command.
2. Division of Labor: Tasks are divided into specific roles, ensuring specialization and efficiency in job performance.
3. Departmentalization: Employees are grouped based on similar tasks, functions, or objectives. This could include departments such as marketing, finance, operations, and human resources.
4. Span of Control: This determines how many employees a manager supervises. A narrow span allows for close supervision, while a wide span promotes autonomy among employees.
5. Coordination and Integration: Mechanisms are established to ensure that different departments and teams work collaboratively toward shared goals.
Organizations can adopt various structures depending on their size, goals, and industry. Below are some of the most common types:
In a functional structure, employees are grouped based on their specific skills and roles. For example, all marketing personnel are in one department, and finance personnel are in another. This structure promotes expertise within departments but can lead to silos, where departments may struggle to collaborate.
A divisional structure organizes the company into semi-autonomous units based on products, services, geographic regions, or customer segments. Each division operates like its own business with separate resources. While this structure fosters specialization, it can result in duplication of resources.
The matrix structure blends functional and divisional models. Employees report to both a functional manager and a project or product manager. While this promotes collaboration and flexibility, it can create confusion due to dual reporting lines.
Flat structures have few or no levels of middle management, resulting in a more egalitarian approach. Decision-making is decentralized, which encourages employee involvement. However, as organizations grow, this structure may become challenging to manage.
A traditional hierarchical structure features a clear chain of command, starting with senior management at the top and descending through various levels. This is one of the most common structures, especially in large organizations, as it ensures clear authority and accountability.
This modern approach relies on outsourcing and partnerships. The organization functions as a central hub, coordinating activities with external entities. While cost-effective, managing external relationships can be challenging.
1. Clarity and Accountability: Clearly defined roles and responsibilities ensure employees understand their tasks and who to report to, reducing confusion.
2. Efficiency: Specialization within departments or teams ensures that tasks are completed efficiently and with expertise.
3. Scalability: A structured framework allows organizations to grow systematically without becoming chaotic.
4. Improved Communication: Structures that promote inter-departmental coordination ensure smooth communication across the organization.
5. Adaptability: Flexible structures, such as the matrix or network models, allow organizations to respond quickly to market changes and challenges.
While a well-designed organizational structure is critical for success, it comes with its own set of challenges:
1. Silos and Isolation: Functional or hierarchical structures can create barriers between departments, hindering collaboration.
2. Over-complexity: In large organizations, overly complex structures can lead to inefficiencies and slower decision-making.
3. Resistance to Change: Employees and managers may resist structural changes due to fear of losing authority or adapting to new roles.
4. Resource Duplication: In divisional structures, resources such as marketing or IT may be duplicated across divisions, leading to higher costs.
5. Conflict in Dual Reporting: Matrix structures, while flexible, can create tension between functional and project managers, impacting productivity.
Organizations must consider several factors when designing their structure:
1. Size of the Organization: Larger organizations typically require more complex structures to manage operations effectively.
2. Nature of the Business: A manufacturing company may adopt a hierarchical structure, while a tech startup might prefer a flat structure for innovation.
3. Business Goals: Companies focused on growth may adopt a divisional or matrix structure to enable expansion.
4. External Environment: Industries with rapidly changing conditions may need flexible structures, like a network or matrix model, to remain competitive.
5. Technological Advancements: Technology influences communication and workflow, prompting organizations to adopt modern, decentralized structures.
The rise of remote work, globalization, and digital transformation has reshaped traditional organizational structures. Companies are increasingly adopting hybrid models, combining in-person and remote teams. Additionally, agile structures, which emphasize adaptability and continuous improvement, are gaining popularity. These approaches prioritize collaboration, innovation, and employee empowerment.
An organizational structure serves as the backbone of any organization, shaping its operations, culture, and success. While no single structure fits all, understanding the various types and their advantages helps organizations choose the best framework for their unique needs. As businesses continue to evolve, adaptability and innovation in structuring will remain critical to achieving long-term goals.
Please register to comment.
With these components in place, your business...
Open the Listing model file located in the ap...
Discover promising partnership opportunities in various industries.
Pitch Your Startup | Find Partners
Comments